B.Tech. I & II Semester
Examination, December 2024
Grading System (GS)
Max Marks:
70 | Time: 3 Hours
Note:
i) Attempt any five questions.
ii) All questions carry equal marks.
a) What do you understand by dependent and independent sources? Explain with neat sketches. How can we convert a voltage source into a current source? Discuss. (Unit 1)
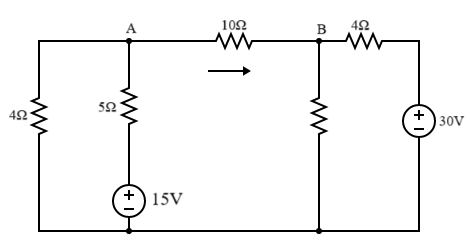
b) Using Nodal Analysis, find the current through the 10Ω resistor in the figure shown below: (Unit 1)
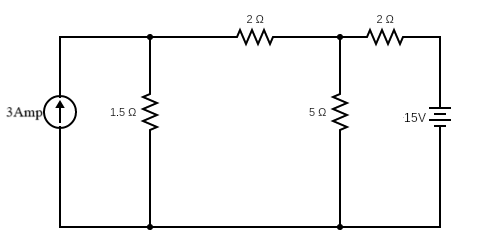
a) Find the value of current in branch AB using the Superposition Theorem.
Refer to the circuit below: (Unit 1)
b) Define the average value, RMS value, form factor, and peak factor of an AC quantity. How are these parameters calculated for a sinusoidal waveform? (Unit 2)
a) A coil of resistance 10Ω and inductance 0.1H is connected in series
with 150µF capacitor across a 200V, 50Hz supply. Calculate: (Unit 2)
i) Inductive reactance
ii) Capacitive reactance
iii) Impedance
iv) Current
v) Power factor
vi) Voltage across the coil
vii) Voltage across capacitor
b) A 3-Φ balanced system supplies 110V to a delta connected load whose phase impedance is (3.54 + j3.54)Ω. Determine the line current and draw the phasor diagram. (Unit 2)
a) What do you understand by self inductance and mutual inductance? Derive the relation between them. (Unit 3)
b) Discuss the laws of electromagnetic induction. (Unit 3)
a) Open circuit and short circuit tests on a single-phase transformer gave
the following results: (Unit 3)
$$ V_0 = 200V,\ I_0 = 0.7A,\ W_0 = 20W \quad \text{(Primary side)} $$
$$ V_s = 10V,\ I_s = 10A,\ W_s = 40W \quad \text{(Secondary side)} $$
Determine the equivalent circuit parameters referred to the primary side.
b) Discuss the construction and working principle of a three-phase induction motor. Draw the torque-slip characteristics. Why can't this motor operate at synchronous speed? (Unit 4)
a) Describe a D.C. machine with suitable sketches, focusing on its main parts and construction details. (Unit 4)
b) A three-phase 440V, 50hp, 50Hz induction motor delivers rated output at 1440 rpm. Calculate: (Unit 4)
i) Number of poles
ii) Synchronous speed
iii) Slip
iv) Slip rpm
v) Rotor speed with respect to:
1) Rotor structure
2) Stator
3) Stator rotating mmf
vi) Rotor EMF at operating speed, if stator to rotor turn ratio is 1:0.5 (Assume winding factor is
unity)
a) Solve for x: (Unit 5)
i) $ (257)_{10} = (x)_2 $
ii) $ (21.625)_{10} = (x)_8 $
iii) $ (BC.2)_{16} = (x)_8 $
iv) $ (33)_{10} = (201)_x $
b) With the help of input and output characteristics, explain the operation of a BJT in common emitter configuration. (Unit 5)
Write short notes on any two:
a) Star Delta Transformation (Unit 1)
b) J-K Flip-Flop (Unit 5)
c) Magnetization Characteristics of Ferromagnetic Material (Unit 3)
d) Power in balanced and unbalanced three-phase systems (Unit 2)