B.Tech. III Semester
Examination, December 2023
Grading System (GS)
Max Marks:
70 | Time: 3 Hours
Note:
i) Attempt any five questions.
ii) All questions carry equal marks.
a) Construct a Binary tree for the given traversals: (Unit 3)
Postorder Traversal: K, D, I, E, A, G, B, F, C, J, H
Inorder Traversal: D, K, I, B, A, E, G, H, J, F, C
Also, find the Preorder traversal of the Binary tree so formed.
b) How a tree can be stored in the memory? Explain with an example. Explain the advantages and disadvantages of the array representation of a tree. (Unit 3)
a) Construct an expression tree for the following algebraic expression: (Unit 3)
$(3a-b)^{2}(4c+2d)^{3}$
b) Explain the Binary Search Tree with an example. Make a Binary Search Tree for the following sequence of numbers, show all steps: (Unit 3)
45, 32, 90, 34, 68, 72, 15, 24, 30, 66, 11, 50, 10. Also, delete 45, 90 and 11 (successively).
Also, write an algorithm to insert an element into a Binary Search Tree.
a) Define AVL Trees. Explain its rotation operations with example. Construct AVL Tree by inserting the following data: (Unit 3)
14, 17, 11, 7, 53, 4, 13, 12, 8, 60, 19, 16, 20
b) Define Huffman tree and describe an algorithm to create a Huffman tree. Construct a Huffman Tree for data structures with its optimal code. (Unit 3)
a) Explain in detail about the graph traversal techniques with suitable example. (Unit 4)
b) Consider the following undirected graph. (Unit 4)
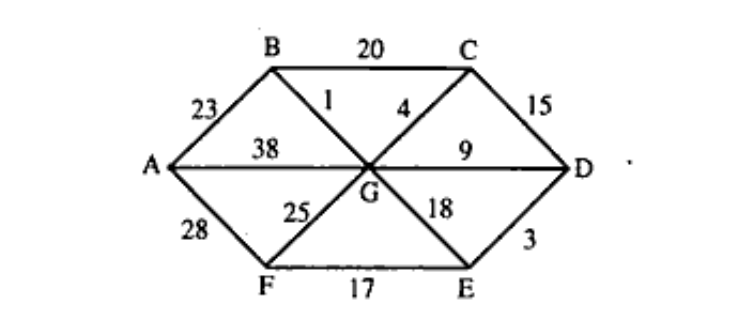
i) Find the adjacency list representation of the graph.
ii) Find a minimum cost spanning tree by Kruskal's algorithm.
a) Write the algorithm to create a heap and sort the following elements using heap sort: (Unit 5)
12, 8, 10, 6, 4, 10, 6, 11, 9, 8, 14, 1, 2
b) How do you implement a circular queue in C using array? Write routines to implement operations for it. Differentiate between Linear Queue and Circular Queue. (Unit 2)
Define doubly linked list. Describe an algorithm to insert an element at the beginning of the doubly linked list. Describe an algorithm to delete an element from the end of doubly linked list. Also explain the advantages and disadvantages of doubly linked list. (Unit 1)
a) Given a 2D array A[-100:100, -5:50]. Find the address of element A [99, 49] considering the base address 10 and each elements requires 4 bytes for storage. Follow row-major order. (Unit 1)
b) What do you understand by stable and in-place sorting? (Unit 5)
c) Define Extended binary tree with example. (Unit 3)
a) Define hash function. Discuss various methods used for resolving hash collisions. (Unit 5)
b) Suppose multidimensional arrays A and B are declared as A(-2:2, 2:22) and B(1:8, 5:5, -10:5) stored in row major order. (Unit 1)
i) Find the length of each dimension of A and B.
ii) The number of elements in A and B.
iii) Assuming Base address (B) $=500,$ $W=2$ Find the effective indices $E_{1}$ $E_{2}$ $E_{3}$ and address of the element B [3, 3, 3].