B.Tech. III Semester
Examination, December 2023
Grading System (GS)
Max Marks: 70 | Time: 3 Hours
Note:
i) Answer any five questions.
ii) All questions carry equal marks.
iii) In case of any doubt or dispute the English version question should be treated as final.
a) Define Data Structures. With the aid of a neat diagram describe the classification of data structures. (Unit 1)
b) What is asymptotic analysis? Explain Big-oh notation. Analyse and write the running time complexity of the following function. (Unit 1) $$ \begin{aligned} &A() \{ \\ &\quad \text{int } i, j, k, n; \\ &\quad \text{for}(i=1; i<=n; i++) \\ &\quad \quad \text{for}(j=1; j*j<=n; j++) \\ &\quad \quad \quad \text{for}(k=1; 2*k<=n; k++) \\ &\quad \quad \quad \quad \text{printf("*");} \\ &\} \end{aligned} $$
a) Given an array with both positive and negative numbers, find the two elements such that their sum is closest to zero. For the below array, algorithm should give -80 and 85. Example: 1, 60, 10, 70, -80, 85. Also discuss the complexity of the process and suggest an alternate way to optimize the complexity. (Unit 2)
b) Consider a two-dimensional array A of order $[20^{*}5]$. The base address of the array is 840, words per memory cell is 8. Find the address of A [15, 3] using row major and column major addressing. (Unit 2)
a) What is a link list? Discuss the advantages of using link list; also write about the various operations which can be performed on link list with their time complexities. (Unit 4)
b) Suppose there are two singly linked lists both of which intersect at some point and become a single linked list as shown below: (Unit 4)
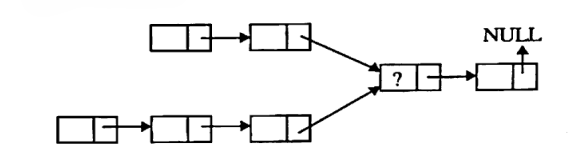
The head pointers of both the lists are known. Give an algorithm for finding the merging point and write the running time complexity.
a) Define Stack. What are the different operations, which can be performed on stack. Explain why Stack is a recursive data structure? (Unit 3)
b) Write an algorithm for evaluating a postfix expression and apply the same for the given postfix expression: $4-5^{*}+77/+$ showing the content of stack at each step. (Unit 3)
a) Explain the importance of queue. Describe why it is a bad idea to implement a linked list version a queue which uses the head of the list as the rear of the queue. (Unit 3)
b) What is the advantage of circular queue over ordinary queue? Write a C program to simulate the working of circular queue of integers using array. Provide the following operations: i) Insert ii) Delete iii) Display. (Unit 3)
a) Show the steps of quick sort on the following set of elements. 26, 56, 47, 36, 13, 95, 85, 32. Assume the last element as the pivot element. (Unit 2)
b) Design a data representation which sequentially map 'n' data objects into an array a [1, n], $n_{1}$ of these data objects are stacks and the remaining are queues. Write algorithms to add and delete elements from these objects. (Unit 3)
a) What is collision? What are the methods to resolves collision? Using the hash function 'key mod 7', insert the following sequence of keys in the hash table- 32, 50, 700, 140, 76, 85, 46, 92, 70, 73 and 101. Use separate chaining technique for collision resolution. (Unit 2)
b) What are L-L, L-R and R-R rotation? Write procedure for adding and deleting a node from the balanced tree and leave the resulting tree balanced. (Unit 5)
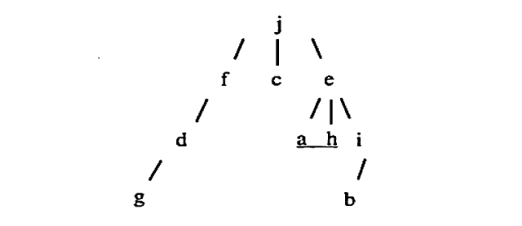
a) What is the sequence of nodes visited for the following tree for a preorder, postorder, and breadth first traversal? (Unit 5)
b) What is Graph traversal? Discuss the difference between traversing a graph and a tree. Consider the following graph. Among the following sequences, which are the depth-first traversals of the above graph? Justify your answer by showing the adjacency list and stack contents for the traversals. (Unit 5)
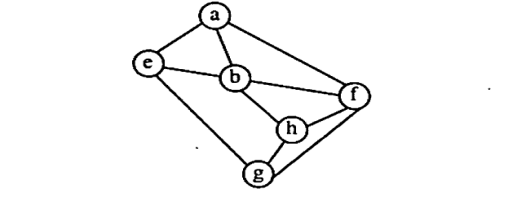
i) abeghf
ii) abfehg
iii) abfhge
iv) afghbe