Rajiv Gandhi Proudyogiki Vishwavidyalaya, Bhopal
New Scheme Based On AICTE Flexible Curricula
Computer Science & Information Technology | III-Semester
Unit 1: Set Theory, Relation, Function, Theorem Proving Techniques
Set Theory: Definition of sets, countable and uncountable sets, Venn Diagrams, proofs of some general identities on sets.
Relation: Definition, types of relation, composition of relations, Pictorial representation of relation, Equivalence relation, Partial ordering relation, Job-Scheduling problem.
Function: Definition, type of functions, one to one, into and onto function, inverse function, composition of functions, recursively defined functions, pigeonhole principle.
Theorem proving Techniques: Mathematical induction, Proof by contradiction.
Previous Years questions appears in RGPV exam.
Q.1) Consider three sets $A = \{1, 2, 3, 4, 5\}$, $B = \{3, 4, 5, 6\}$ and $C = \{1, 5, 7\}$. Using Venn diagrams, determine and shade the regions corresponding to $(A \cup B) \cap (B \cap C)$ and $A \cap (B \cup C)$. Verify if these expressions are equivalent by listing the elements. (June-2025)
Q.2) Define and illustrate an equivalence relation by constructing an equivalence relation on the set $S = \{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6\}$ where two elements are related if they have the same remainder when divided by 3. (June-2025)
Q.3) What is pigeonhole principle? Prove it by using mathematical induction and use it to show that in a group of 15 people, at least two share the same birth month. (June-2025)
Q.4) Write short notes on: Partial Ordering Relation. (June-2025)
Write short notes on: Countable and uncountable sets. (June-2025)
Q.5) Define various types of functions. How many symmetric and reflexive relations are possible from a set A containing ‘n’ elements? (Dec-2024)
Q.6) Define Pigeon hole Principle. Write the contra positive of the implication: "if it is Sunday then it is a holiday." (Dec-2024)
Q.7) Prove that the relation $R$ defined by "a is congruent to b modulo m" on the set of integers is an equivalence relation. (June-2024)
Q.8) Prove that $5^{2n} - 1$ is divisible by 24, where $n$ is any positive integer. (June-2024)
Q.9) Show that the relation 'R' defined by $(a, b) R (c, d)$ iff $a + d = b + c$ is an equivalence relation. (June-2024)
Q.10) Out of 120 students surveyed, it was found that 20 students have studied French, 50 students have studied English, 70 students have studied Hindi, 5 have studied English and French, 20 have studied English and Hindi, 10 have studied Hindi and French, only 3 students have studied all the three languages. Find how many students have studied: i) Hindi alone ii) French alone iii) English, but not Hindi iv) Hindi, but not French. (Dec-2023)
Q.11) If $R$ be a relation in the set of integers $\mathbb{Z}$ defined by $R = \{(x, y) : x \in \mathbb{Z}, y \in \mathbb{Z}, (x - y) \text{ is multiple of } 3\}$. Show that it is an equivalence relation. (Dec-2023)
Q.12) If $f : \mathbb{R} \to \mathbb{R}$ is defined by: $$ f(x) = \begin{cases} 3x - 12, & x > 3 \\ 2x^2 + 3, & -2 < x \le 3 \\ 3x^2 - 7, & x \le -2 \end{cases} $$ Find $f^{-1}(3)$, $f^{-1}(0)$, and $f^{-1}(-2)$. (Dec-2023)
Q.13) Show that $1^2 + 2^2 + 3^2 + \dots + n^2 = \dfrac{n(n+1)(2n+1)}{6}, \quad n \ge 1$ by mathematical induction. (Dec-2023)
Q.14) Prove that $P(A) \subseteq P(B)$ if and only if $A \subseteq B$. (June-2023)
Q.15) Suppose that $R$ is the relation on the set of strings of English letters such that $aRb$ if and only if $l(a) = l(b)$, where $l(x)$ is the length of the string $x$. Is $R$ an equivalence relation? (June-2023)
Q.16) Illustrate the concept of an inverse function. Let $f : Z \to Z$ be such that $f(x) = x + 1$. Is $f$ invertible? if it is then what is its inverse? (June-2023)
Q.17) Show that the relation 'R' defined by $(a, b) R (c, d)$ if $a + d = b + c$ is an equivalence relation. (Nov-2022)
Q.18) If $X = \{1, 2, 3, 4\}$ and $R = \{(x, y) | x < y\}$. Draw the graph of 'R' and also give its matrix. (Nov-2022)
Q.19) Prove that if R is an equivalence relation on a set A, show that $R^{-1}$ is also an equivalence relation on A. (Nov-2022)
Q.20) What is Mathematical induction? Use mathematical induction to prove that: $ 1.1! + 2.2! + \dots + n.n! = (n + 1)! - 1 $ where $n$ is a positive integer. (Nov-2022)
Q.21) Explain the method of proving theorems by direct, indirect, contradiction and by cases. (Nov-2022)
Expected Sample Questions for Future Exams
Q.1) Let $f: A \to B$ and $g: B \to C$ be two functions. Prove that if $f$ and $g$ are one-to-one, then $g \circ f$ is also one-to-one. (Predicted)
Q.2) Define Partial Ordering Relation. Draw the Hasse Diagram for the divisibility relation on the set $\{1, 2, 4, 8, 16\}$. (Predicted)
Q.3) Explain the Job-Scheduling problem with an example involving partial ordering. (Predicted)
Q.4) Use Mathematical Induction to prove that $1 + 3 + 5 + \dots + (2n-1) = n^2$ for all $n \ge 1$. (Predicted)
Q.5) Define an Equivalence Relation. Prove that the intersection of two equivalence relations on a set $A$ is also an equivalence relation. (Predicted)
Unit 2: Algebraic Structures
Algebraic Structures: Definition, Properties, types: Semi Groups, Monoid, Groups, Abelian group, properties of groups, Subgroup, cyclic groups, Cosets, factor group, Permutation groups, Normal subgroup.
Homomorphism and Isomorphism: Homomorphism and isomorphism of Groups, example and standard results.
Rings and Fields: Definition and standard results.
Previous Years questions appears in RGPV exam.
Q.1) Prove that the set $G = \{0, 1, 2, 3\}$ under addition modulo 4 is an abelian group. Identify the identity and inverse elements. (June-2025)
Q.2) Define a homomorphism between two groups. Verify whether the mapping $f: \mathbb{R} \to \mathbb{R}$ defined by $f(x) = 2x$ is a homomorphism under addition. (June-2025)
Q.3) Write short notes on: Permutation group. (June-2025)
Q.4) Let Z be the group of integers with binary operation * defined by $a * b = a + b - 2$, for all $a, b \in Z$. Find the identity element of the group $\langle Z, * \rangle$. (Dec-2024)
Q.5) Show that every Cyclic group is Abelian. (Dec-2024)
Q.6) What is Ring? Define elementary properties of Ring with example. (Dec-2024)
Q.7) Prove or disprove that intersection of two normal subgroups of a group G is again a normal subgroup of G. (Dec-2024)
Q.8) Let $Z$ be the group of integers with binary operation $*$ defined by $a * b = a + b - 2$, for all $a, b \in Z$. Find the identity element of the group $\langle Z, * \rangle$. (June-2024)
Q.9) Show that every Cyclic group is Abelian. (June-2024)
Q.10) Prove that $G = \{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6\}$ is an abelian group of order 7 with respect to addition modulo 7. (June-2024)
Q.11) Prove or disprove that intersection of two normal subgroups of a group G is again a normal subgroup of G. Define subgroup, normal subgroup, Quotient group, with an example for each. (June-2024)
Q.12) Prove that $F = \{a + b\sqrt{2} \mid a, b \text{ are rational}\}$ is a field. (Dec-2023)
Q.13) Define the following: i) Symmetric Group ii) Normal Subgroup iii) Homomorphism. (Dec-2023)
Q.14) Define group. Explain the properties of groups. (June-2023)
Q.15) Let $S = N \times N$. Let $*$ be the operation on $S$ defined by $(a, b) * (a', b') = (aa', bb')$. i) Define $f : (S, *) \to (Q, \times)$ by $f(a, b) = a/b$. Show that $f$ is a homomorphism. ii) Find the congruence relation $\sim$ in $S$ determined by the homomorphism $f$, that is, where $x \sim y$ if $f(x) = f(y)$. (June-2023)
Q.16) Discuss in brief: Cosets. (June-2023)
Q.17) Let Z be the group of integers with binary operation * defined by $a * b = a + b - 2$, for all $a, b \in Z$. Find the identity element of the group $\langle Z, * \rangle$. (Nov-2022)
Q.18) Prove that the set $G = \{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6\}$ is a finite abelian group of order 7 with respect to multiplication modulo 7 as the composition in G. (Nov-2022)
Q.19) State the Lagrange's Theorem with example. Also explain Permutation and Symmetric Group. (Nov-2022)
Expected Sample Questions for Future Exams
Q.1) Prove that the intersection of two subgroups of a group G is a subgroup of G. (Predicted)
Q.2) Define a Ring. Prove that in a Ring R, $a.0 = 0.a = 0$ for all $a \in R$. (Predicted)
Q.3) Explain the concept of a Monoid with a suitable example. Differentiate between a Monoid and a Group. (Predicted)
Q.4) State and prove Lagrange's Theorem for finite groups. (Predicted)
Q.5) Define a Normal Subgroup. Show that a subgroup $H$ of $G$ is normal if and only if $gHg^{-1} = H$ for all $g \in G$. (Predicted)
Unit 3: Propositional Logic
Propositional Logic: Proposition, First order logic, Basic logical operation, truth tables, tautologies, Contradictions, Algebra of Proposition, logical implications, logical equivalence, predicates, Normal Forms, Universal and existential quantifiers.
Finite State Machine: Introduction to finite state machine, Finite state machines as models of physical system equivalence machines, Finite state machines as language recognizers.
Previous Years questions appears in RGPV exam.
Q.1) Consider the propositions $p$, $q$ and $r$, where: $p$: "It is raining.", $q$: "I am carrying an umbrella.", $r$: "I stay dry." Assume the implication $(p \to q) \to r$. Construct a truth table for the expression $(p \to q) \to r$ and determine if it is a tautology or contradiction. (June-2025)
Q.2) What are predicates in propositional logic? Define universal and existential quantifiers with examples. (June-2025)
Q.3) Write short notes on: Finite state machines as language recognizers. (June-2025)
Q.4) Prove the validity of the following argument "if the races are fixed so the casinos are crooked, then the tourist trade will decline. If the tourist trade decreases, then the police will be happy. The police force is never happy. Therefore, the races are not fixed." (Dec-2024)
Q.5) Explain various Rules of Inference for Propositional Logic. (Dec-2024)
Q.6) i) Prove that $p \land q \Rightarrow q \lor p$ is a Tautology. ii) Show that $(p \lor q) \land (\neg p) \land (\neg q)$ is a contradiction. (June-2024)
Q.7) Explain various Rules of Inference for Propositional Logic. (June-2024)
Q.8) Define Pigeon hole Principle. Write the contra positive of the implication: "if it is Sunday then it is a holiday." (June-2024)
Q.9) Construct the truth table of the following formula: i) $(\sim(p \lor (q \lor r)) \Leftrightarrow ((p \lor q) \land (p \lor r)))$ ii) $((\sim q \Rightarrow \sim p) \Rightarrow (p \Rightarrow q))$. (Dec-2023)
Q.10) Write the negation of the following: i) If the determinant of a system of linear equations is zero then either the system has no solution or has an indefinite number of solutions. ii) Either today is not a Sunday or today is not a Wednesday. (Dec-2023)
Q.11) Show that the proposition $\sim(p \land q)$ and $\sim p \lor \sim q$ are logically equivalent. (Dec-2023)
Q.12) Obtain the conjunctive normal form (CNF) of: i) $p \land (p \Rightarrow q)$ ii) $\sim p \Rightarrow [r \land (p \Rightarrow q)]$. (Dec-2023)
Q.13) Show that the $((p \lor q) \land \neg p) \to q$ compound proposition is a tautology. (June-2023)
Q.14) Use existential and universal quantifiers to express the statement. "No one has more than three grandmothers" using the propositional function $G(x, y)$, which represents "$x$ is the grandmother of $y$." (June-2023)
Q.15) Discuss the 6 tuple notation of finite state machine $M$ with an example. (June-2023)
Q.16) Discuss in brief: Disjunctive normal form. (June-2023)
Q.17) i) Prove that $p \land q \Rightarrow q \lor p$ is a Tautology. ii) Show that $(p \lor q) \land (\sim p) \land (\sim q)$ is a contradiction. (Nov-2022)
Q.18) Find PDNF by constructing its PCNF of $(Q \vee P) \wedge (Q \vee R) \wedge (\sim(P \vee R) \vee \sim Q)$. (Nov-2022)
Q.19) Prove that for any three propositions P, Q, R the compound proposition $(P \to (Q \to R)) \to ((P \to Q) \to (P \to R))$ is a tautology by laws of logic. (Nov-2022)
Q.20) Explain Tautologies, Contradiction and Contingencies with suitable examples. (Nov-2022)
Expected Sample Questions for Future Exams
Q.1) What is a Mealy Machine? How is it different from a Moore Machine? (Predicted)
Q.2) Convert the following expression into Principal Disjunctive Normal Form (PDNF): $(P \land Q) \lor (\neg P \land R)$. (Predicted)
Q.3) Explain the concept of Logical Equivalence with an example involving De Morgan's Laws. (Predicted)
Q.4) Test the validity of the argument: "If it rains, the ground is wet. The ground is not wet. Therefore, it did not rain." using Rules of Inference. (Predicted)
Q.5) Differentiate between a Tautology, a Contradiction, and a Contingency with truth table examples. (Predicted)
Unit 4: Graph Theory
Introduction: Basic terminology of graphs, Planar graphs, Multigraphs and weighted graphs.
Connectivity & Paths: Isomorphic graphs, Paths, Cycles and connectivity, Shortest path in weighted graph.
Advanced Paths: Introduction to Eulerian paths and circuits, Hamiltonian paths and circuits.
Coloring & Isomorphism: Graph coloring, chromatic number, Isomorphism and Homomorphism of graphs.
Previous Years questions appears in RGPV exam.
Q.1) Define graph theory and explain the basic terminology of graphs such as vertices, edges, degree and adjacency. (June-2025)
Q.2) Define and give an example of an isomorphic graph pair. Verify isomorphism between two adjacency matrices. (June-2025)
Q.3) For the graph $G$ with vertices $V = \{A, B, C, D\}$ and edges $E = \{(A, B), (B, C), (C, D), (D, A), (A, C)\}$, determine: i) Whether the graph contains a Eulerian path or circuit or not. ii) All Hamiltonian circuits in the graph G. (June-2025)
Q.4) Show that there does not exist a graph with 5 vertices with degrees 1, 3, 4, 2, 3 respectively. (Dec-2024)
Q.5) Explain complete digraph. (Dec-2024)
Q.6) Define planar graph. Prove that for any connected planar graph, $v - e + r = 2$ Where $v, e, r$ is the number of vertices, edges, and regions of the graph respectively. (Dec-2024)
Q.7) Discuss about Complete digraph and Euler Graph with the help of suitable examples. (Dec-2024)
Q.8) Explain the following: i) Euler Graph ii) Isomorphic graphs iii) Minimal spanning tree iv) Height of the tree. (June-2024)
Q.9) Explain complete digraph and Euler Graph using suitable example of both. (June-2024)
Q.10) Define planar graph. Prove that for any connected planar graph, $v - e + r = 2$ where $v, e, r$ is the number of vertices, edges, and regions of the graph respectively. (June-2024)
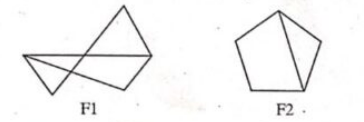
Q.11) Determine whether the graphs $F_1$ and $F_2$ are isomorphic. (Dec-2023)
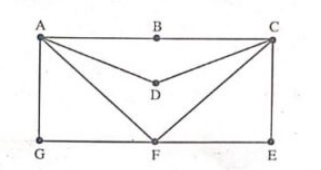
Q.12) Find an Euler Path in the graph below. (Dec-2023)
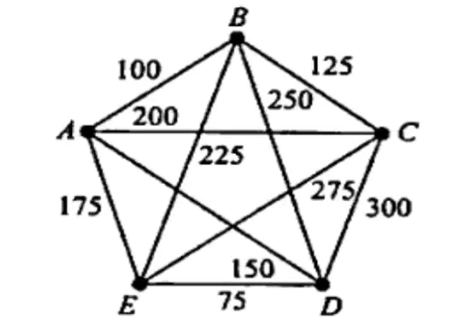
Q.13) Consider the complete weighted graph $G$ in the following figure with 5 vertices. Find a Hamiltonian circuit of minimal weight. (June-2023)
Q.14) Discuss the various applications of graph colouring. (June-2023)
Q.15) State Euler’s formula for a planar graph. Give an example of a planar graph with 5 vertices and 5 regions and verify Euler’s formula for your example. (June-2023)
Q.16) Explain complete digraph and Euler Graph using suitable example of both. (Nov-2022)
Q.17) Define planar graph. Prove that for any connected planar graph, $v - e + r = 2$ Where $v, e, r$ is the number of vertices, edges, and regions of the graph respectively. (Nov-2022)
Q.18) Give a simple condition on the weights of a graph that will guarantee that there is a unique maximal spanning tree for the graph. (Nov-2022)
Q.19) Define Isomorphism of graphs. What are the steps followed in discovering the Isomorphism? (Nov-2022)
Q.20) Explain Eulerian and Hamiltonian graphs with examples, also draw the graphs of the following: i) Eulerian but not Hamiltonian ii) Hamiltonian but not Eulerian. (Nov-2022)
Q.21) Prove that the sum of the degree of all the vertices in a graph G is equal to twice the number of edges in G. (Nov-2022)
Expected Sample Questions for Future Exams
Q.1) State and explain Kuratowski's two graphs ($K_5$ and $K_{3,3}$) and their role in determining planarity. (Predicted)
Q.2) Find the chromatic number of a complete graph $K_n$ and a bipartite graph $K_{m,n}$. (Predicted)
Q.3) Explain Dijkstra's algorithm for finding the shortest path in a weighted graph with an example. (Predicted)
Q.4) Prove the Handshaking Lemma: In any graph, the sum of degrees of all vertices is equal to twice the number of edges. (Predicted)
Q.5) Explain the difference between Prim's and Kruskal's algorithm for finding a Minimum Spanning Tree (MST). (Predicted)
Unit 5: Posets, Lattices, Combinatorics, Recurrence Relations
Posets, Hasse Diagram and Lattices: Introduction, ordered set, Hasse diagram of partially ordered set, isomorphic ordered set, well ordered set, properties of Lattices, bounded and complemented lattices.
Combinatorics: Introduction, Permutation and combination, Binomial Theorem, Multimonial Coefficients.
Recurrence Relation and Generating Function: Introduction to Recurrence Relation and Recursive algorithms, Linear recurrence relations with constant coefficients, Homogeneous solutions, Particular solutions, Total solutions, Generating functions, Solution by method of generating functions.
Previous Years questions appears in RGPV exam.
Q.1) Explain a recursively defined function. Solve the recurrence relation $f(n) = f(n-1) + 3$ with initial condition $f(0) = 2$. (June-2025)
Q.2) How many permutations can be formed from the letters of the word “MATHEMATICS” such that all vowels are together? (June-2025)
Q.3) What is a Hasse diagram? Draw the Hasse diagram for the set $\{1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18\}$ with the divisibility relation. (June-2025)
Q.4) Define a lattice and prove that every finite lattice has a unique least upper bound and greatest lower bound. (June-2025)
Q.5) Write short notes on: Binomial theorem. (June-2025)
Q.6) Prove that a lattice with 5 elements is not a Boolean algebra. (Dec-2024)
Q.7) Obtain the generating function for the sequence 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4. (Dec-2024)
Q.8) Find the numbers between 1 to 500 that are not divisible by any of the integers 2 or 3 or 5 or 7. (Dec-2024)
Q.9) A collection of 10 electric bulbs contain 3 defective ones. (i) In how many ways can a sample of four bulbs be selected? (ii) In how many ways can a sample of 4 bulbs be selected which contain 2 good bulbs and 2 defective ones? (iii) In how many ways can a sample of 4 bulbs be selected so that either the sample contains 3 good ones and 1 defectives ones or 1 good and 3 defectives ones? (Dec-2024)
Q.10) Solve the following recurrence equation using generating function. $G(K) - 7 G(K-1) + 10 G(K-2) = 8K + 6$. (Dec-2024)
Q.11) Let $(L, \vee, \wedge, \leq)$ be a distributive lattice and $a, b \in L$. if $a \wedge b = a \wedge c$ and $a \vee b = a \vee c$ then show that $b = c$. (Dec-2024)
Q.12) Prove that the Complement of each element in a Boolean Algebra B is unique. (June-2024)
Q.13) Let $A$ be any finite set and $P(A)$ be the power set of $A$. $\subseteq$ be the inclusion relation on the elements of $P(A)$. Draw the Hasse diagrams of $(P(A), \subseteq)$ for the following: i) $A = \{a\}$ ii) $A = \{a, b\}$ iii) $A = \{a, b, c\}$ iv) $A = \{a, b, c, d\}$. (June-2024)
Q.14) Draw the Hasse diagram representing the positive divisors of 36 and 45. (June-2024)
Q.15) Prove that a lattice with 5 elements is not a Boolean algebra. (June-2024)
Q.16) Define a lattice. Let $(L, \le, \lor, \land)$ be a lattice, and $a, b, c, d \in L$ be such that $a \le b$ and $c \le d$. Show that $a \lor c \le b \lor d$ and $a \land c \le b \land d$. (Dec-2023)
Q.17) Show that $D_{12}$ and $D_{18}$ are isomorphic lattices. Further, show that none is isomorphic to the lattice $D_{20}$. (Dec-2023)
Q.18) Show that $a_n = c_1 2^n + c_2 4^n$ is a solution of the recurrence relation $a_n - 6a_{n-1} + 8a_{n-2} = 0$. (Dec-2023)
Q.19) Find the sequence having the generating function $G(x)$ given by: $$ G(x) = \frac{x}{1 - 2x} $$ (Dec-2023)
Q.20) Consider the set $A = \{4, 5, 6, 7\}$. Let $R$ be the relation $\le$ on $A$. Draw the directed graph and the Hasse diagram of $R$. (June-2023)
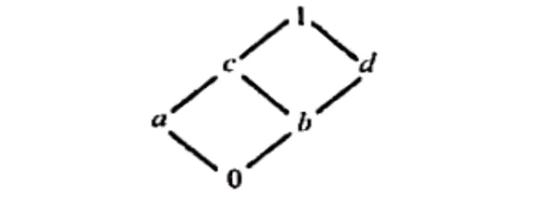
Q.21) Consider the lattice $M$ in the following figure. i) Find the non-zero join irreducible elements and atoms of $M$. ii) Is $M$ distributive and complemented? (June-2023)
Q.22) Find the explicit formula for the Fibonacci numbers. Use $f_n = f_{n-1} + f_{n-2}$ as recursive condition and $f_0 = 0$ and $f_1 = 1$ as initial condition. (Nov-2022)
Q.23) Draw the Hasse diagram representing the positive divisors of 36. (Nov-2022)
Expected Sample Questions for Future Exams
Q.1) Solve the recurrence relation $a_n = 2a_{n-1} + 3a_{n-2}$ with initial conditions $a_0 = 1, a_1 = 1$. (Predicted)
Q.2) Show that the lattice of divisors of 30, $D_{30}$, is a Boolean Algebra. (Predicted)
Q.3) Find the number of distinct permutations of the letters in the word "MISSISSIPPI". (Predicted)
Q.4) Solve the recurrence relation $a_n - 7a_{n-1} + 10a_{n-2} = 0$ using the method of Generating Functions. (Predicted)
Q.5) Explain the concept of a Complemented Lattice and a Distributive Lattice with Hasse diagrams. (Predicted)